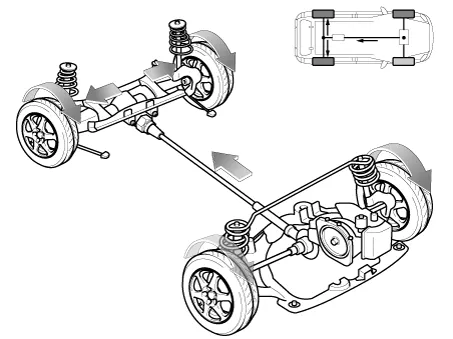
Hyundai Santa Fe (TM): Coupling Assembly / Direct Electro Hydraulic Actuator Coupling. Description and operation
Hyundai Santa Fe (TM) 2019-2023 Service and Repair Manual / 4 Wheel Drive (4WD) System / Coupling Assembly / Direct Electro Hydraulic Actuator Coupling. Description and operation
| Description |
4WD ECU processes signals from various sensors and determines the current road
and driving conditions. The ECU then utilizes this information to implement
precision control over the 4WD coupling's multi-plate clutch and variably adjust
the amount of torque delivered tothe rear wheels.
Four Wheel Drive (4WD) transfer mode selection
| 1. |
AUTO MODE:
|
| 2. |
LOCK MODE:
|
Electronic Coupling - 4WD Control (By Driving Condition)
| 1. |
Cruising (Auto Mode)
|
| 2. |
Cornering (Auto Mode)
|
| 3. |
Wheel Slip (Auto Mode)
|
| Operation |
| Electronic Coupling |
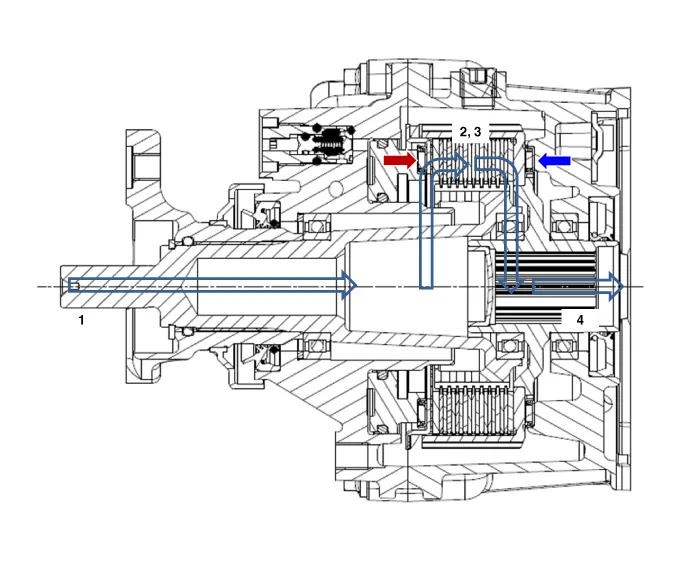
| 1. |
The power is delivered in the following order:
Transmission -> Transfer -> Propeller shaft
|
| 2. |
AWD ECU calculates the necessary amount of rear-wheel torque and sends
the corresponding driving current to the actuator (electronic motor
and hydraulic pump).
|
| 3. |
The piston operates by the oil pressure and the friction is generated.
Then, the clutch is engaged.
|
| 4. |
The power is delivered to the differential by the engaged clutch and
the driving power is generated in to the rear wheel.
|
Component Location 1. Relif valve 2. Pressure sensor 3. Oil hydraulic motor 4. Coupling assembly
Inspection • All units are filled up with coupling fluid (ultra-low viscosity ATF) prior to shipping.
Other information:
Hyundai Santa Fe (TM) 2019-2023 Service and Repair Manual: Heater & A/C Control Unit (DATC). Components and components location
Hyundai Santa Fe (TM) 2019-2023 Service and Repair Manual: Troubleshooting
Trouble Symptom Charts Trouble Symptom 1 Trouble Symptom 2 Trouble symptom Probable cause Remedy The set vehicle speed varies greatly upward or downward "Surging" (repeated alternating acceleration and deceleration) occurs after set
Categories
Copyright © 2025 www.hsafe4.com - 0.0143