Hyundai Santa Fe (TM): Emission Control System
Description and operation
| Description |
| • |
The Crankcase Emission Control System prevents blow-by gas from releasing
into the atmosphere. This system recycles gas back into the intake manifold
(Closed Crankcase Ventilation Type).
|
| • |
The Evaporative Emission Control System prevents evaporative gas from
releasing into the atmosphere. This system burns gas at appropriate
engine operating condition after gathering it in the canister.
|
| • |
The Exhaust Emission Control System converts the three pollutants [hydrocarbons
(HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen (NOx)] into harmless
substances by using the 3-way catalytic converter.
|
Components and components location
| Components Location |
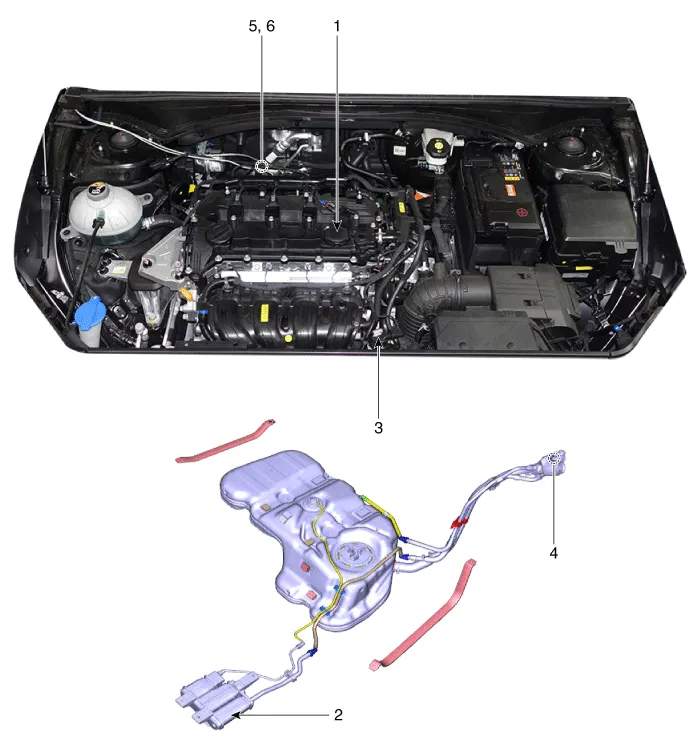
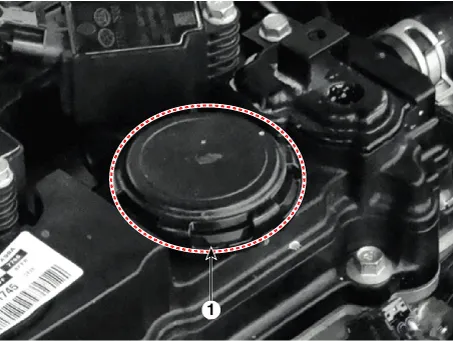
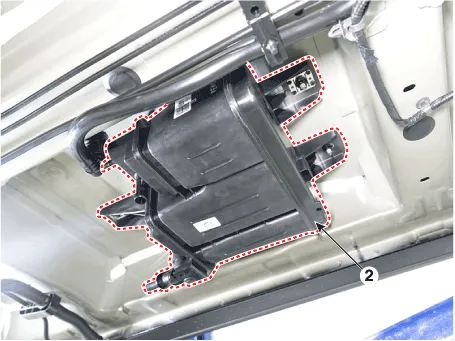
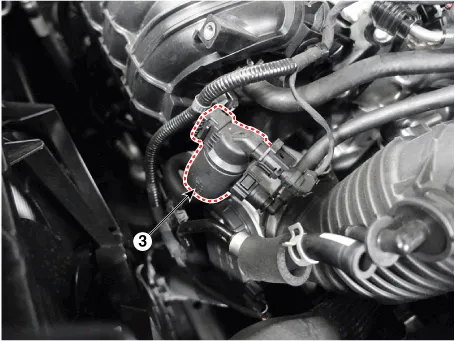
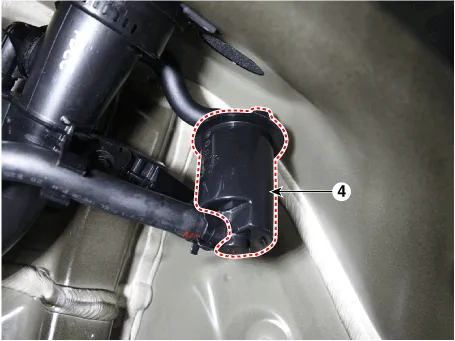
| 1. Crankcase
pressure regulating valve (PRV) 2. Canister 3. Purge control solenoid valve (PCSV) |
4. Fuel tank
air filter 5. Catalytic converter (WCC) 6. Catalytic converter (UCC) |
|
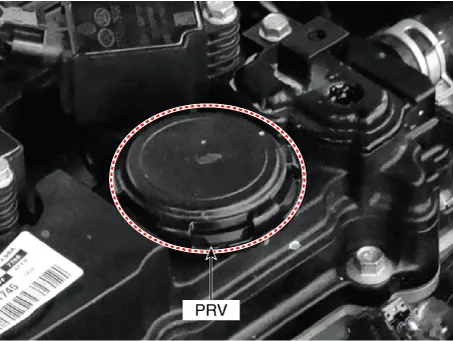
1. Crankcase Pressure Regulating Valve (PRV) |
2. Canister |
|
|
|
|
3. Purge control solenoid valve (PCSV) |
4. Fuel tank air filter |
|
|
|
|
5. Catalytic converter (WCC) |
6. Catalytic converter (UCC) |
|
|
|
Troubleshooting
| Troubleshooting |
|
Symptom |
Suspect area |
|
Engine will not start or hard to start |
Vapor hose damaged or disconnected |
|
Engine struggles to start |
Malfunction of the Purge Control Solenoid Valve |
|
Rough idle or engine stalls |
Vapor hose damaged or disconnected |
|
Malfunction of the PCV valve |
|
|
Rough idle |
Malfunction of the Evaporative Emission Control System |
|
Excessive oil consumption |
Positive crankcase ventilation line clogged |
Specifications
| Specifications |
|
Item |
Specification |
|
Coil Resistance (Ω) |
20.0 - 22.0 [20°C (68°F)] |
Schematic diagrams
| Schematic Diagram |
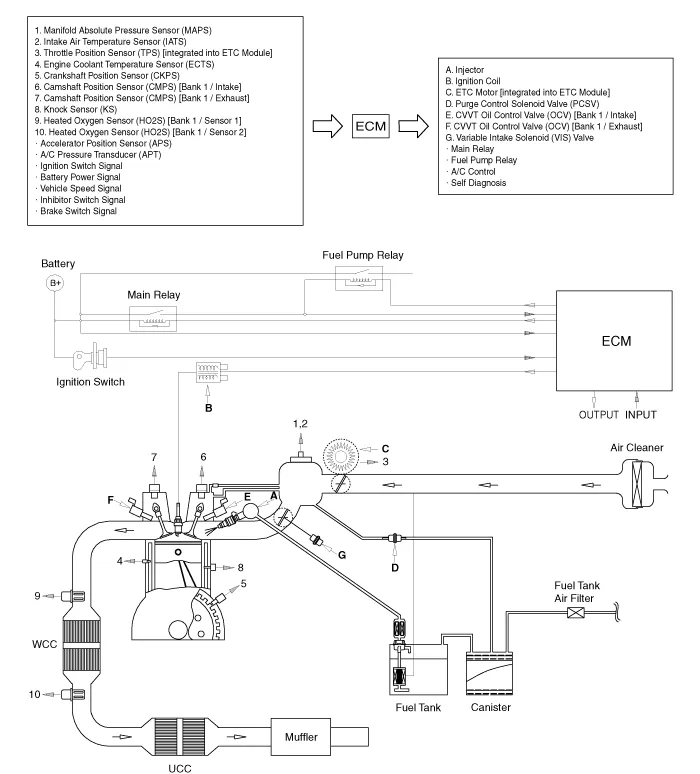
Crankcase Emission Control System
Schematic diagrams
| Schematic Diagram |
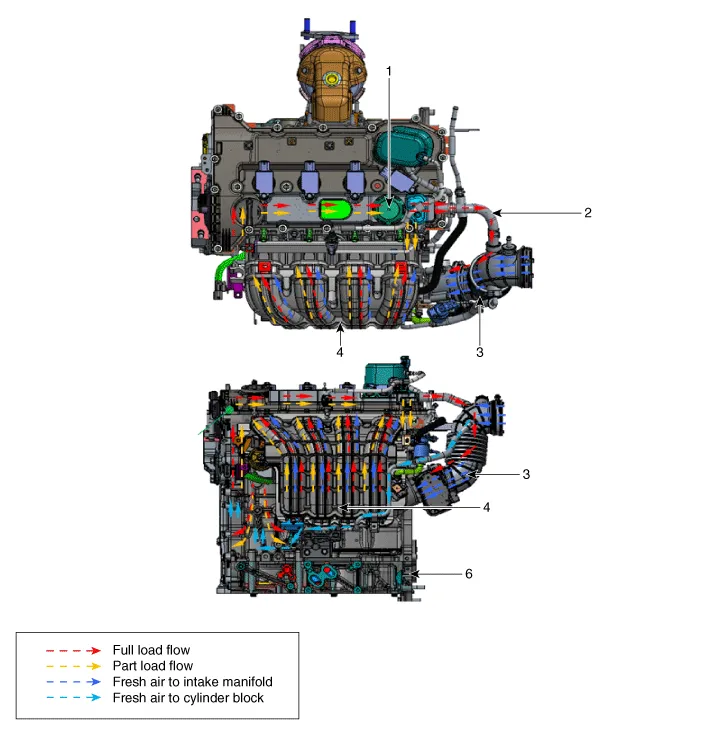
| 1. PCV Valve 2. Breather hose 3. Air intake hose |
4. Intake maifold 5. Air breather hose 6. Cylinder block |
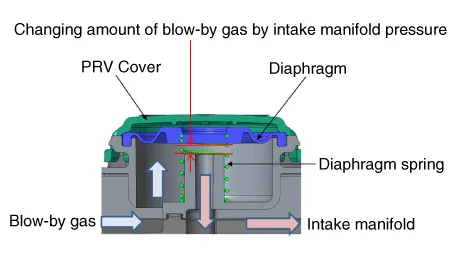
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) Valve. Description and operation
| Description |
| Operation Principle |
|
Engine Condition |
Stop |
Idle or Deceleration |
Normal operating condition |
Accelerating in the high load area |
|
Intake manifold pressure |
0 |
High |
Appropriate |
Low |
|
PRV (Diaphragm) |
Full open |
A little open |
Appropriate open |
Considerable open |
|
Amount of blow-by gas |
0 |
A little |
Middle |
A lot |
|
Diaphragm component part |
|
|||
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) Valve. Repair procedures
| Removal |
| 1. |
Remove the cylinder head cover.
(Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "Cylinder Head Cover")
|
| Installation |
| 1. |
Install in the reverse order of removal.
|
Crankcase Check Valve. Repair procedures
| Removal and Installation |
|
| 1. |
Disconnect the battery (-) terminal.
|
| 2. |
Remove the engine room under cover.
(Refer to Engine And Transaxle Assembly - "Engine Room Under Cover")
|
| 3. |
Remove the drive belt.
(Refer to Drive Belt System - "Drive Belt")
|
| 4. |
Remove the compressor mounting bolts.
(Refer to Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning - "Compressor")
|
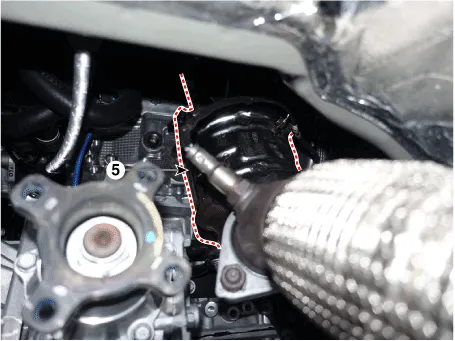
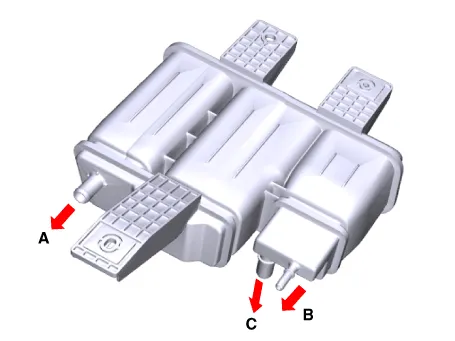
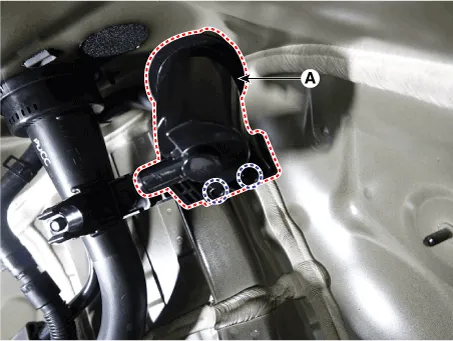
| 5. |
Disconnect the crankcase check valve hose (A) and then remove the crankcase
check valve (B).
|
Evaporative Emission Control System
Description and operation
| Description |
Schematic diagrams
| Schematic Diagram |
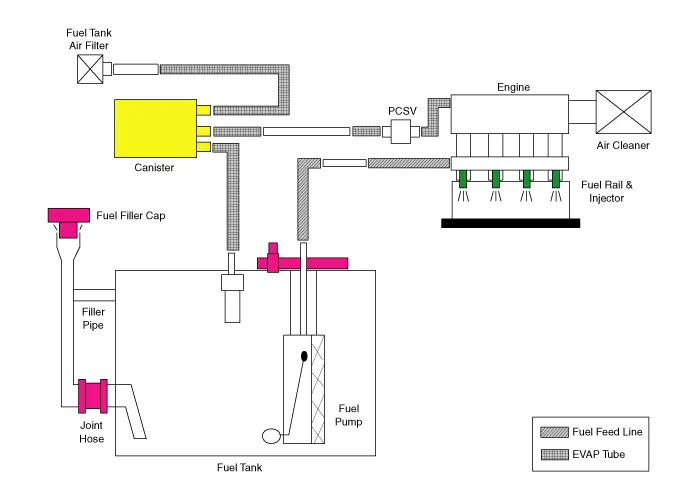
Canister. Repair procedures
| Removal |
|
| 1. |
Turn the ignition switch OFF and disconnect the battery (-) terminal.
|
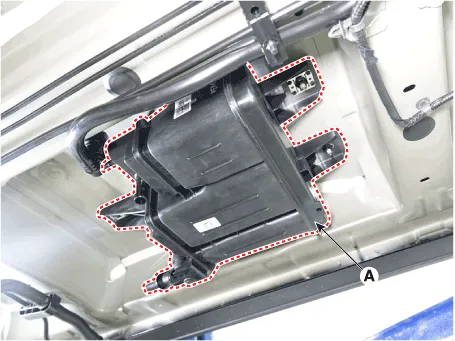
| 2. |
Remove the floor under cover (A).
|
| 3. |
Disconnect the vent hose (A).
|
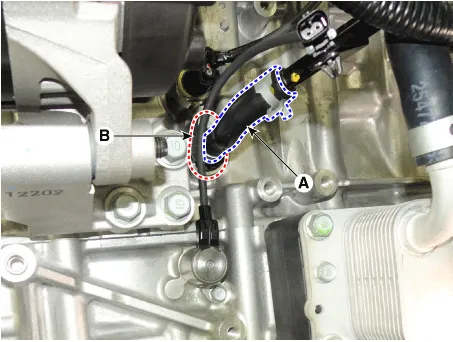
| 4. |
Disconnect the vapor hose quick-connector (A).
|
| 5. |
Remove the canister (A) after loosening the mounting nuts.
|
| Installation |
| 1. |
Install in the reverse order of removal.
|
| Inspection |
| 1. |
Check for the following items visually.
A : Canister ↔ Atmosphere
B : Canister ↔ Fuel Tank
C : Canister ↔ Intake Manifold
|
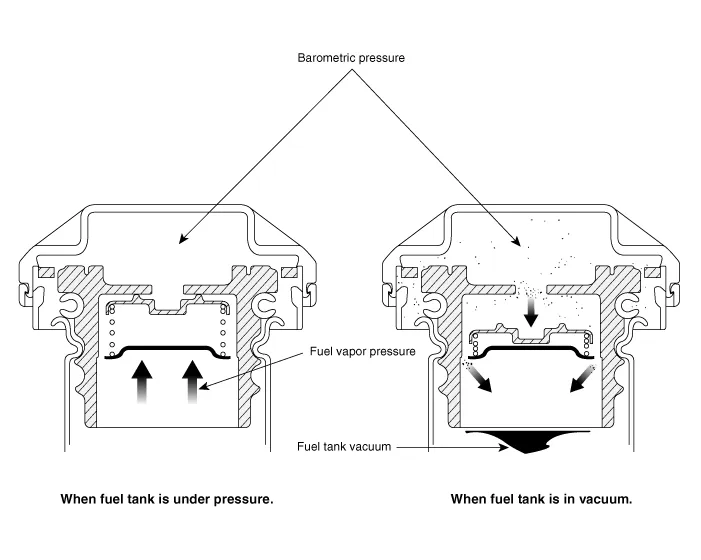
Fuel Filler Cap. Description and operation
| Description |
Fuel Tank Air Filter. Repair procedures
| Removal |
|
| 1. |
Turn the ignition switch OFF and disconnect the battery (-) terminal.
|
| 2. |
Lift the vehicle.
|
| 3. |
Remove the rear-left wheel & tire and wheel house cover.
|
| 4. |
Separate the ventilation hoses (A).
|
| 5. |
Remove the fuel tank air filter (A) after loosening the mounting bolts.
|
| Installation |
| 1. |
Install in the reverse order of removal.
|
Exhaust Emission Control System
Description and operation
| Description |
| 1. |
Open Loop air/fuel ratio is controlled by information pre-programmed
into the ECM.
|
| 2. |
Closed Loop air/fuel ratio is constantly adjusted by the ECM based on
information supplied by the oxygen sensor.
|
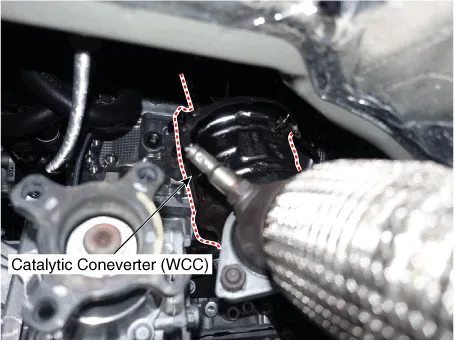
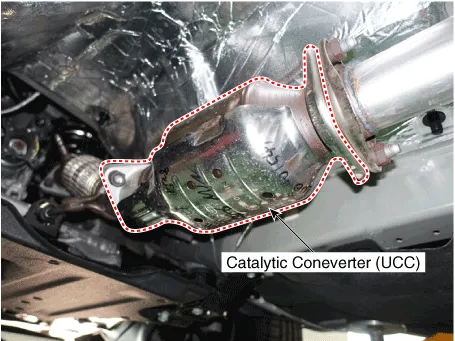
Catalytic Converter. Description and operation
| Description |
Catalytic Converter. Repair procedures
| Removal |
| 1. |
Remove the exhaust manifold.
(Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "Exhaust Manifold")
|
| 1. |
Remove the Center Muffler.
(Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "Center Muffler")
|
| Installation |
| 1. |
Install in the reverse order of removal.
|
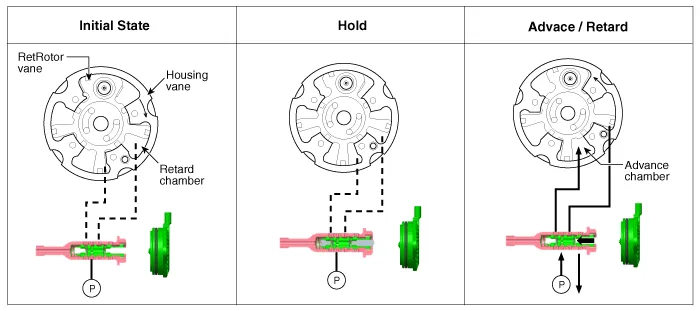
CVVT (Continuously Variable Valve Timing) System. Description and operation
| Description |
| – |
the CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) which supplies the engine oil to the
cam phaser or runs out the engine oil from the cam phaser in accordance
with the ECM PWM (Pulse With Modulation) control signal,
|
| – |
the CVVT Oil Temperature Sensor (OTS) which measures the engine oil
temperature,
|
| – |
and the Cam Phaser which varies the cam phase by using the hydraulic
force of the engine oil.
|
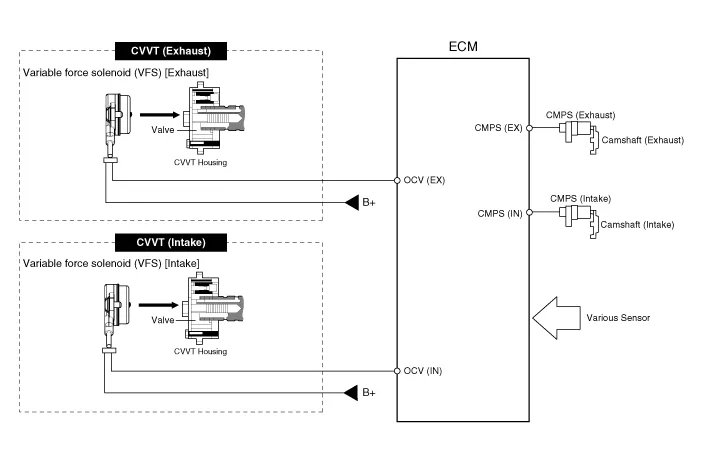
| Operation Principle |
|
| [CVVT System Mode] |
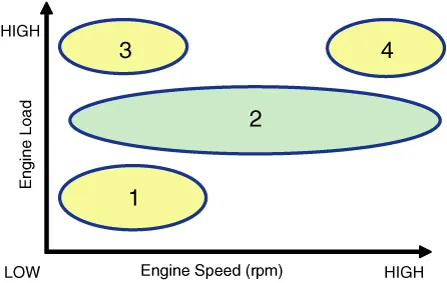
|
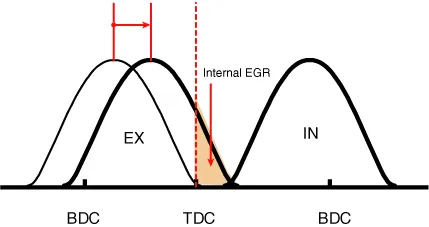
(1) Low Speed / Low Load |
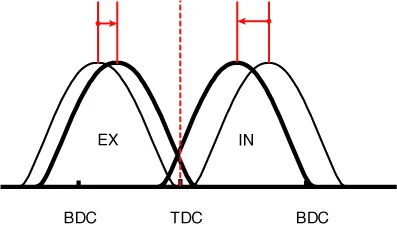
(2) Part Load |
|
|
|
|
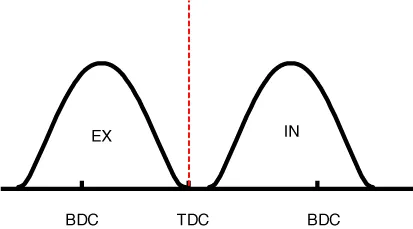
(3) Low Speed / High Load |
(4) High Speed / High Load |
|
|
|
|
Driving Condition |
Exhaust Valve |
Intake Valve |
||
|
Valve Timing |
Effect |
Valve Timing |
Effect |
|
|
(1) Low Speed /Low Load |
Completely Advance |
* Valve Under-lap * Improvement of combustion stability |
Completely Retard |
* Valve Under-lap * Improvement of combustion stability |
|
(2) Part Load |
Retard |
* Increase of expansion work * Reduction of pumping loss * Reduction of HC |
Retard |
* Reduction of pumping loss |
|
(3) Low Speed /High Load |
Retard |
* Increase of expansion work |
Advance |
* Prevention of intake back flow (Improvement of volumetric efficiency) |
|
(4) High Speed /High Load |
Advance |
* Reduction of pumping loss |
Retard |
* Improvement of volumetric efficiency |
Description and operation Description The ignition coil is a kind of small transformer that transforms the battery voltage to 30 kV or more to create a spark in the spark plug gap in the cylinder.
Other information:
Hyundai Santa Fe (TM) 2019-2023 Service and Repair Manual: Power Door Locks
Components and components location Component Location 1. Driver power window main switch 2. IBU (Integrated Body Control Unit) 3. Door lock switch 4. Tailgate lock actuator & switch 5. Front door lock actuator & switch 6.
Hyundai Santa Fe (TM) 2019-2023 Service and Repair Manual: Controller
Heater & A/C Control Unit (Manual). Components and components location Component Connector Pin Function Pin No Connector A Connector B 1 Battery Low 2 ISG B+ Common 3
Categories
- Manuals Home
- Hyundai Santa Fe Owners Manual
- Hyundai Santa Fe Service Manual
- Engine Control/Fuel System
- Components and components location
- Auto Hold. Warning messages
- New on site
- Most important about car